Audio Codec Configuration in RCVx3 Router
Overview
The Audio Configuration feature in the RCVx3 Router allows users to set up and manage audio codecs, optimize voice transmission, and ensure high-quality audio communication over VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) networks. It provides various configuration options such as selecting codec types, adjusting packet cycles, enabling echo cancellation, and configuring DTMF (Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency) settings.
These settings are crucial for achieving optimal voice clarity, low latency, and efficient bandwidth usage based on the network conditions and VoIP requirements.
How It Works
Audio configuration in VoIP relies on audio codecs, which compress and decompress voice signals for transmission over IP networks. The router supports multiple codec types, allowing flexibility based on the available bandwidth and required voice quality.
When a VoIP call is made, the codec negotiation process determines the codec to be used between the calling and receiving devices. The router follows a priority order for codec selection, ensuring compatibility with the remote endpoint.
The key parameters in the RCVx3 Audio Configuration include:
-
Audio Codec Types – Determines how voice data is encoded and transmitted.
-
Payload Size – Defines the size of the compressed audio data in packets.
-
Packet Cycle – Specifies how often audio packets are transmitted.
-
Echo Cancellation – Reduces echoes to improve call clarity.
-
Auto Gain Control – Adjusts volume levels dynamically.
-
DTMF Configuration – Ensures proper signal transmission for touch-tone inputs.
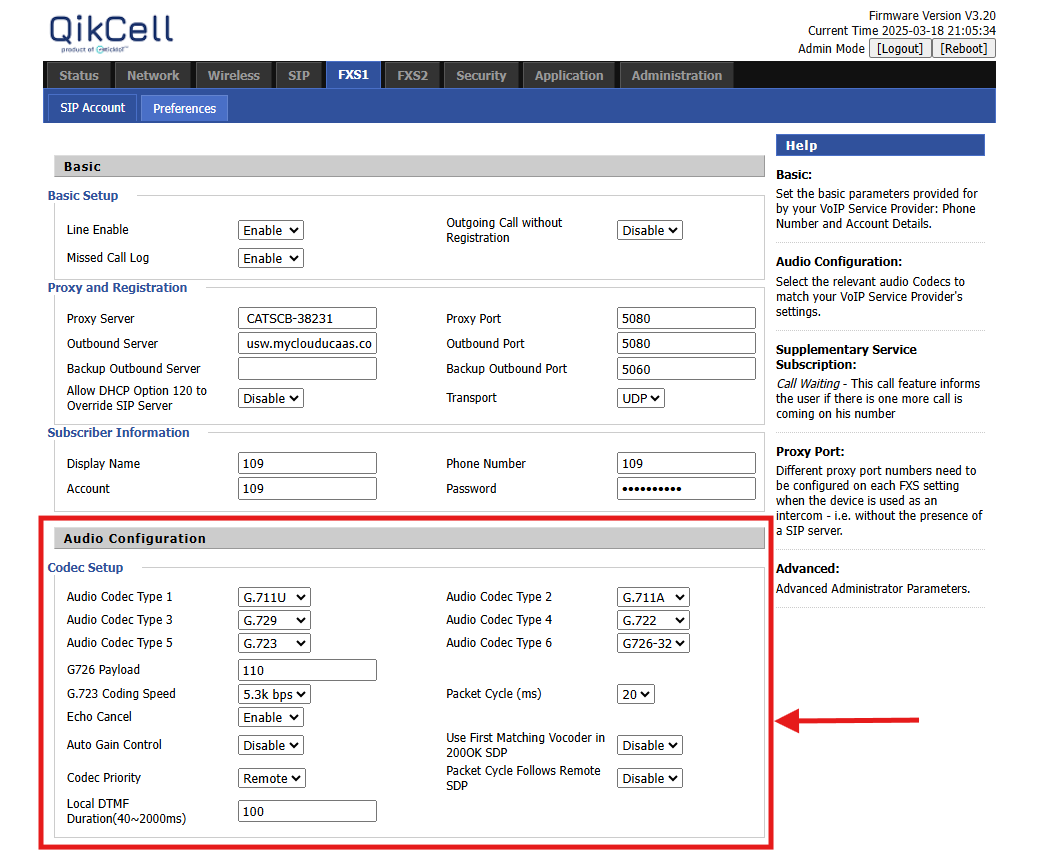
Key Audio Configuration Settings
1. Codec Setup
The router supports multiple audio codec types, each designed for different use cases. The available codecs are:
Codec Type |
|
| ||||||
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
🔹 Example Usage:
-
If a business wants high-quality calls, it should use G.711U or G.722.
-
If the network has low bandwidth, G.729 or G.723 is a better choice.
-
A call center with multiple simultaneous calls may use G.726-32 to optimize bandwidth usage.
2. Payload & Packet Cycle
-
G726 Payload: 110
This defines the payload size for the G.726 codec. A larger payload reduces overhead but may increase latency. -
G.723 Coding Speed: 5.3 kbps
This setting controls the bit rate at which the G.723 codec encodes audio. Lower bit rates help save bandwidth but may reduce voice quality. -
Packet Cycle (ms): 20
The packet cycle determines how often voice packets are sent. A lower value (e.g., 20ms) ensures real-time voice transmission with minimal delays.
🔹 Example Usage:
-
A packet cycle of 20ms is optimal for reducing latency in voice calls.
-
A call over G.723 at 5.3 kbps would be ideal for a low-bandwidth rural VoIP network.
3. Echo Cancellation & Auto Gain Control
-
Echo Cancel: Enabled
Echo cancellation removes unwanted audio reflections that occur during VoIP calls. -
Auto Gain Control: Disabled
This feature automatically adjusts microphone sensitivity. It is disabled by default, but users can enable it if they experience volume inconsistencies.
🔹 Example Usage:
-
If a user hears their own voice echoing, enabling Echo Cancellation prevents it.
-
In an environment where callers have varying speaking volumes, enabling Auto Gain Control ensures even volume levels.
4. Codec Negotiation & Prioritization
-
Use First Matching Vocoder in 200OK SDP: Disabled
When disabled, the router negotiates the best possible codec instead of forcing the first matching one. -
Codec Priority: Remote
This setting means the router follows the codec preference of the remote party instead of enforcing its own. -
Packet Cycle Follows Remote SDP: Disabled
If enabled, the router would adopt the packet cycle from the remote device. Keeping it disabled ensures local control over packet transmission.
🔹 Example Usage:
-
If a business wants full control over codec selection, they should set Codec Priority to Local.
-
If they trust the remote system’s settings, leaving Remote priority enabled ensures seamless interoperability.
5. DTMF Configuration
-
Local DTMF Duration: 100 ms (Range: 40–2000 ms)
This setting defines how long DTMF tones (keypad signals) last. It should be adjusted based on IVR (Interactive Voice Response) systems that require precise tone durations.
🔹 Example Usage:
-
If a user experiences delays in keypress recognition during automated calls, increasing the DTMF duration may resolve the issue.
-
If DTMF is too slow, reducing the duration to 40-60ms speeds up response times.
Use Cases of Audio Configuration
-
Enterprise VoIP Deployment – Ensuring HD-quality voice calls for businesses with stable internet.
-
Call Centers – Optimizing bandwidth usage with compressed codecs like G.729.
-
Telecom Networks – Adapting to different VoIP infrastructure by prioritizing remote codec settings.
-
Remote Work Communication – Using echo cancellation and auto gain control for better audio clarity.
-
IVR Systems – Adjusting DTMF settings for seamless interaction with automated voice menus.
Final Notes
-
The default settings provided in the RCVx3 Router are optimized for most VoIP scenarios.
-
Customers can modify these settings based on their network conditions, bandwidth availability, and voice quality requirements.
-
For high-quality voice calls, use G.711U or G.722.
-
For low-bandwidth networks, use G.729 or G.723.
-
If echo issues occur, ensure Echo Cancellation is enabled.
-
Adjust DTMF duration if keypad inputs are delayed or unrecognized.
Related Articles
FAX Configuration in RCVx3 Router
Overview The FAX Configuration feature in the RCVx3 Router is designed to support the reliable transmission of fax data over an IP network. Since traditional fax machines were originally built for analog telephone lines, sending a fax over a digital ...LED indication of RCVx3 Router
The LED's on the router indicate the router's current status. Solid Green Light on Cellular, Wifi, WAN, LAN The solid green lights on a router typically indicate the following statuses for different connections: Cellular (Mobile Network) Light: Solid ...Firmware Upgrade in RCVx3 Router using Local UI
The Firmware Upgrade feature for the RCVx3 device allows administrators to update the device's firmware to the latest version, ensuring access to new features, security patches, and performance improvements. This process is simple and secure, ...How to configure FXS1/FXS2 SIP Account settings using Local UI
To configure the SIP Account Settings in the RCVx3 device, please follow the steps outlined below. 1. Open a web browser and enter the URL of the RCVx3 device: 192.168.3.1. 2. If you are logging in for the first time, use the default credentials: ...How to configure FXS1/FXS2 Preference settings using Local UI
To configure the Preference Settings in the RCVx3 device, please follow the steps outlined below. 1. Open a web browser and enter the URL of the RCVx3 device: 192.168.3.1. 2. If you are logging in for the first time, use the default credentials: ...